According to statistics from the World Health Organization, cancer is the second leading threat to human health. Among the top ten causes of death worldwide, cancer ranks second. By detecting cancer biomarkers, it is possible to identify cancer at an early stage and significantly improve the chances of a cure. For example, PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) testing aids in the early detection of prostate cancer. During treatment, tracking changes in cancer biomarkers can help evaluate therapeutic efficacy and guide timely adjustments to treatment plans. For instance, AFP (Alpha-Fetoprotein) levels can indicate the effectiveness of liver cancer treatment. Cancer biomarker testing is also valuable for monitoring recurrence—regular testing allows for the early detection of tumor regrowth and prompt intervention.
The Role of the Cancer Biomarker Assay Kit
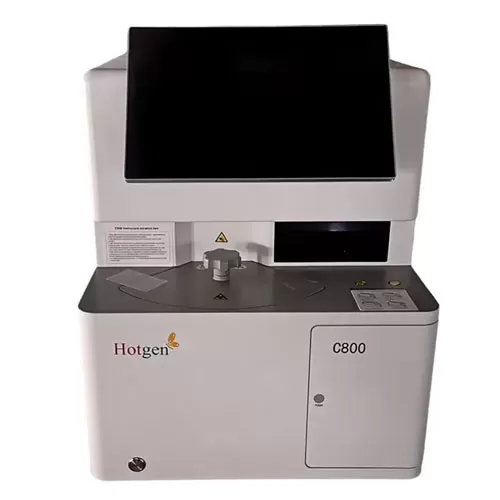
The Cancer Biomarker Assay Kit plays a crucial role in cancer diagnosis and treatment. It detects biological markers on the surface of cancer cells, enabling assessment of cancer severity and progression trends. This information supports targeted therapy and reduces the risk of recurrence or metastasis. Additionally, it provides important references for comprehensive cancer treatment and has been widely applied in clinical practice, including in the detection of prostate and liver cancers.
Companion diagnostic reagents are particularly significant in cancer drug development, as they help identify suitable patients and support new drug discovery. Genetic testing for personalized cancer therapy provides genetic profiles and precision medication strategies tailored to each patient.
How to Use the Cancer Biomarker Assay Kit
Sample Collection
Blood: Collect venous blood using a sterile needle and collection tube.
Sample Processing
Follow the kit instructions for sample preparation, such as centrifugation of blood samples.
Reagent Preparation
Prepare reagents according to the instructions, ensuring they are within their expiration dates and correctly mixed.
Sample Testing
Mix the processed sample with the appropriate reagents, allow reactions to occur as directed, and analyze using the designated testing equipment.
Result Reading and Interpretation
Interpret the results based on the kit guidelines. A positive result typically indicates the presence of cancer biomarkers; a negative result suggests absence or levels below the threshold. Use relevant clinical references for accurate interpretation.
Quality Control
Implement quality control procedures to ensure accuracy and reliability. Follow quality assurance protocols for pathological instruments and reagents.
Documentation and Reporting
Record all relevant test data and report findings to physicians or patients as required.
Follow-Up Actions
Positive results require further diagnostic work-up. For negative results in high-risk individuals, regular retesting is recommended. Handle samples and kits per biohazard protocols, select appropriate screening kits, ensure testing is conducted by trained personnel, maintain patient confidentiality, perform routine maintenance on equipment and kits, and dispose of hazardous materials according to regulations.
The Value of Early Detection
Cancer biomarkers can often be detected through serological testing before any visible imaging changes occur, offering a critical window for early diagnosis and intervention. They also serve as important tools for identifying tumor recurrence, enabling prompt clinical responses.
Hotgen's Cancer Biomarker Assay Kits are specifically optimized for early cancer screening and prognosis monitoring. These kits can detect tumor biomarkers in blood samples before significant imaging changes become apparent—supporting proactive diagnosis, treatment planning, and evidence-based clinical decisions.
 English
English français
français Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español ไทย
ไทย русский
русский português
português العربية
العربية Indonesia
Indonesia